Introduction
In every household, having a well-equipped medicine cabinet is crucial for handling minor injuries and ailments effectively. Whether it’s a small cut, a burn, or a headache, having the right supplies at hand can make a significant difference in how quickly and effectively you can provide first aid. This article explores essential items to keep in your medicine cabinet, ensuring you’re prepared for common emergencies.
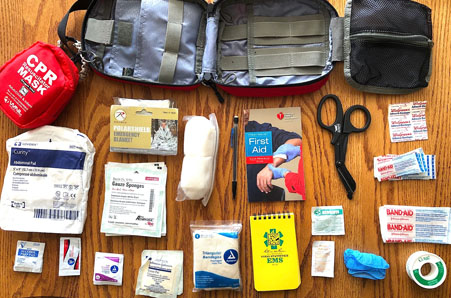
Contents of a Basic First Aid Kit
A basic first aid kit should contain items that address common injuries and illnesses. Here are essential supplies to include:
- Bandages: Different sizes of adhesive bandages and sterile gauze pads.
- Adhesive tape: To secure dressings or bandages.
- Antiseptic wipes: For cleaning wounds.
- Antibiotic ointment: To prevent infection in minor cuts and scrapes.
- Pain relievers: Such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
- Antihistamines: For allergic reactions or insect bites.
- Scissors and tweezers: To assist in wound care and splinter removal.
- Instant cold packs: To reduce swelling or pain from strains or sprains.
- Medical gloves: For protecting both the first aider and the patient.
- First aid manual: To provide guidance on how to respond to emergencies.
Essential Medications to Have
Certain medications are crucial to have in your medicine cabinet for immediate relief:
- Aspirin: For heart attack symptoms.
- Antacids: To relieve heartburn or indigestion.
- Antidiarrheal medications: For managing sudden diarrhea.
- Cough and cold medications: Including decongestants and cough suppressants.
- Allergy medications: Such as epinephrine injectors for severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis).
Managing Burns and Scalds
Burns and scalds are common household injuries. Here’s how to treat them:
- Cool the burn: Hold the burned area under cool (not cold) running water for at least ten minutes.
- Cover the burn: Use sterile gauze or a clean cloth to cover the burn loosely.
- Do not apply ice: Ice can damage the skin and exacerbate the injury.
- Pain relief: Administer over-the-counter pain relievers if needed.
- Seek medical attention: For severe burns, especially those larger than the palm of the hand or involving the face, seek medical help immediately.
Dealing with Cuts and Scrapes
Minor cuts and scrapes can be treated effectively at home:
- Clean the wound: Wash the wound thoroughly with mild soap and water.
- Apply antibiotic ointment: To prevent infection.
- Cover the wound: Use sterile gauze or a bandage to protect the area.
- Change dressings regularly: Especially if the wound continues to seep or becomes dirty.
- Watch for signs of infection: Such as increased redness, swelling, or drainage.
Handling Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe. Here’s what to do:
- Mild reactions: Treat with over-the-counter antihistamines and observe for worsening symptoms.
- Severe reactions (anaphylaxis): Use an epinephrine auto-injector if available, then seek emergency medical help immediately.
Storing Medications Safely
It’s crucial to store medications safely to maintain their effectiveness and prevent accidental ingestion:
- Keep medications in their original containers: This ensures proper labeling and dosage information.
- Store in a cool, dry place: Avoid bathrooms and kitchen cabinets, as humidity can affect medications.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets: Consider using child-proof containers or locks on cabinets.
Checking and Updating Your First Aid Kit
Regularly inspect your first aid kit to ensure it’s well-stocked and supplies have not expired:
- Check expiration dates: Replace any expired medications or supplies promptly.
- Replenish used items: After using supplies, restock to maintain readiness.
- Update for seasonal needs: Consider adding items like sunscreen or insect repellent depending on the season.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many minor injuries and illnesses can be managed at home, certain situations require professional medical attention:
- Severe bleeding: That does not stop with direct pressure.
- Broken bones: Visible deformity or inability to move a limb.
- Loss of consciousness: Even if brief.
- Severe allergic reactions: Especially if accompanied by difficulty breathing.
Conclusion
A well-prepared medicine cabinet can make a significant difference in responding to common health emergencies at home. By ensuring you have the essential supplies and medications, you can handle minor injuries and illnesses promptly and effectively. Regularly review and update your first aid kit to maintain preparedness for any situation.
Table Summary
| Section | Summary |
|---|---|
| Contents of a Basic First Aid Kit | Lists essential items such as bandages, antiseptics, pain relievers, and gloves for addressing common injuries. |
| Essential Medications to Have | Highlights medications like aspirin, antacids, and allergy medications that should be readily available for immediate relief. |
| Managing Burns and Scalds | Provides steps for treating burns, including cooling the burn and covering it with sterile gauze, while emphasizing when to seek medical help. |
| Dealing with Cuts and Scrapes | Offers advice on cleaning and covering minor cuts and scrapes, with tips on monitoring for signs of infection. |
| Handling Allergic Reactions | Discusses how to manage allergic reactions, from mild to severe, including the use of epinephrine for anaphylaxis and the importance of seeking emergency help. |
| Storing Medications Safely | Advises on proper storage practices to maintain medication efficacy and prevent accidental ingestion by children or pets. |
| Checking and Updating Your First Aid Kit | Encourages regular inspection and restocking of first aid kits to ensure readiness for emergencies. |
| When to Seek Professional Help | Outlines situations such as severe bleeding, broken bones, loss of consciousness, and severe allergic reactions that necessitate medical attention. |
FAQ
What should I do if I run out of a specific item in my first aid kit?
Ensure you replenish any used or expired items promptly to maintain your kit’s readiness.
How often should I check the expiration dates of medications in my medicine cabinet?
Check expiration dates regularly, at least every six months, and replace any expired medications.
Can I substitute one type of bandage for another in my first aid kit?
It’s best to keep a variety of bandage types, but in a pinch, any clean, non-adhesive material can be used temporarily.
Should I keep prescription medications in my household first aid kit?
Only if they are prescribed for emergency situations by your healthcare provider. Otherwise, keep them separate and secure.
What should I do if someone accidentally ingests medication from my medicine cabinet?
Contact poison control immediately. Have the container of the ingested substance available for reference.
How can I safely dispose of expired medications from my medicine cabinet?
Many pharmacies have medication disposal programs. Contact your local pharmacy or health department for guidance.
Is it necessary to keep a first aid manual in my kit if I already know basic first aid?
Yes, a manual can provide crucial guidance in stressful situations and may cover scenarios you haven’t encountered.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower you to create a well-equipped and effective first aid setup at home, ensuring you can handle unexpected health situations with confidence.